Table of Content
Such areas make eradication of mites particularly difficult, as the crusts protect the mites from topical miticides/scabicides, necessitating prolonged treatment of these areas. Unrecognized crusted scabies often is the source of institutional outbreaks of scabies. Infection control personnel and dermatologists should be involved as soon as scabies is suspected in an institution. An institution-wide information program should be implemented to instruct all management, medical, nursing, and support staff about scabies, the scabies mite, and how scabies is and is not spread. Scabies may be diagnosed clinically in geographical areas where it is common when diffuse itching presents along with either lesions in two typical spots or itchiness is present in another household member.
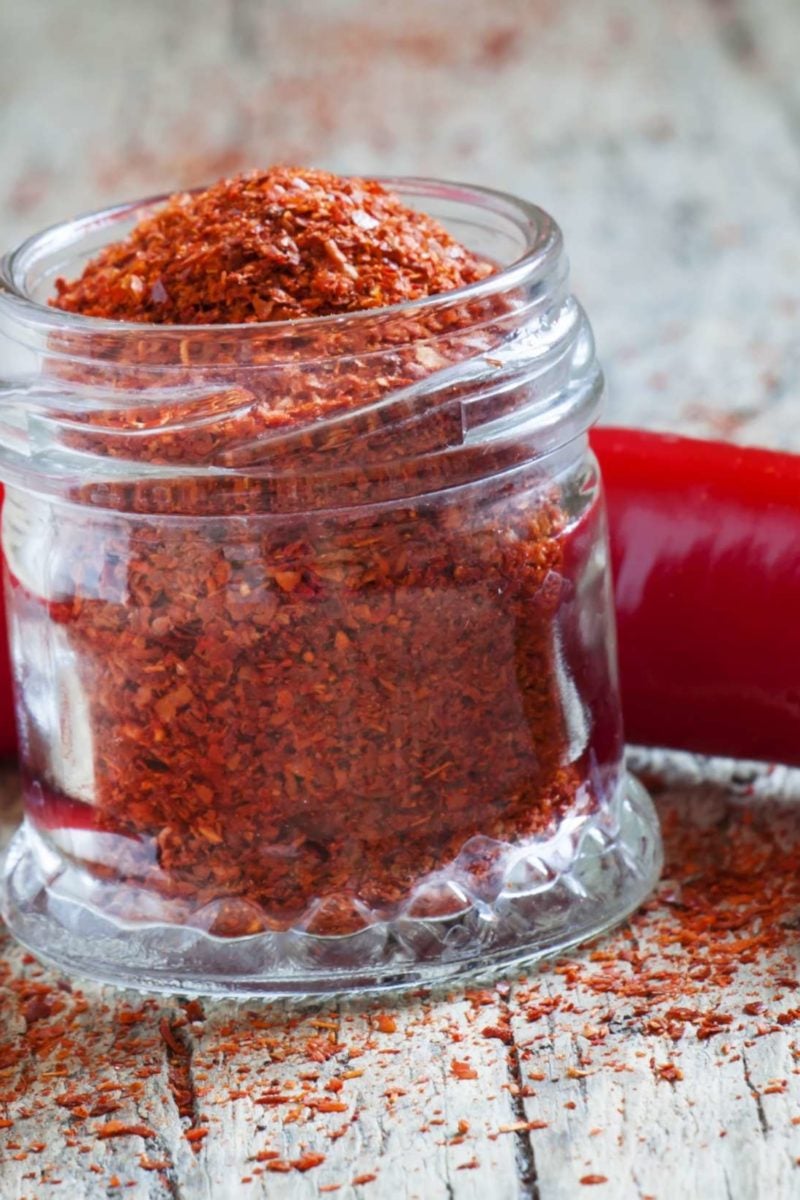
Close contact in a child care center is a fast way for the infestation to spread. Capsaicin has pain-relieving properties and has long been used as a home remedy for burning pain. Though it will not kill the mites, creams made with capsaicin from cayenne peppers may relieve pain and itching by desensitizing your skin to the bothersome bites and bugs. A scabies ink test can help spot burrowed paths in your skin created by the mites. To do this test, your doctor can drop ink from a fountain pen onto an area of the skin that appears to be infested.
Most Read (Last 30 Days)
Join APIC in Indianapolis, Indiana, June 13-15, 2022 for the 50th Annual Conference—the largest gathering in the world of the infection prevention community. Verywell Health uses only high-quality sources, including peer-reviewed studies, to support the facts within our articles. Read our editorial process to learn more about how we fact-check and keep our content accurate, reliable, and trustworthy.
Similarly to washing clothes, vacuuming the house will not cure the infestation that is affecting an individual. However, vacuuming up any mites that could be in floor coverings will help prevent scabies from spreading to other people. Little evidence supports the effectiveness of turmeric in treating scabies.
Crusted scabies
Scabies is contagious and can spread quickly in areas where people are in close physical contact. The hallmark symptoms of scabies include a rash and intense itching that gets worse at night. Continuous scratching of the infected area can create sores that become infected. If this occurs, additional treatment with antibiotics for the skin infection may be recommended. Scabies (pronounced skay-bees) is caused by scabies mites — tiny, insect-like parasites that infect the top layer of your skin. It’s easily spread to other people during skin-to-skin touching.

The animal should receive veterinary treatment for mange. Until successfully treated, patients with crusted scabies should be isolated from other patients who do not have crusted scabies. Assigning a cohort of caretakers to care only for patients with crusted scabies can reduce the potential for further transmission.
Prevention and control of scabies
Areas with a lack of access to water also have higher rates of disease. It typically only occurs in those with a poor immune system and people may have millions of mites, making them much more contagious. In these cases, spread of infection may occur during brief contact or by contaminated objects. The mite is very small and at the limit of detection with the human eye. It is not readily obvious; factors that aid in detection are good lighting, magnification, and knowing what to look for.
Clean the room of patients with crusted scabies regularly to remove contaminating skin crusts and scales, which can contain many mites. All staff and visitors should wear gloves and gowns on entering the single room or when having direct contact with patients suspected or confirmed to have scabies. All staff and visitors should wear gloves and gowns on entering the single room, or when having direct contact with patients suspected or confirmed to have scabies. Guidelines for preventing transmission vary depending on the type of scabies, the number of cases, and the degree and duration of skin exposure that a person has had to an infested person. Bedding, clothing and towels used by infested people any time during the 3 days before treatment should be machine washed and dried using the hot water and hot dryer cycles, or be dry-cleaned.
Essential oils
All new patients and staff should be screened and treated for skin conditions suggestive of possible scabies. The local health department and neighboring institutions should be notified of the outbreak and of any patients who may have been transferred to or of staff who may have worked in other institutions. When a person is first infested with scabies mites, it usually takes 2-6 weeks for symptoms to appear after being infested. If a person has had scabies before, symptoms appear 1-4 days after exposure.
Scabies sometimes is spread indirectly by sharing items such as clothing, towels, or bedding used by an infested person. People who develop crusted scabies, also known as Norwegian scabies, often need repeat treatments to get rid of the mites. Use hot, soapy water to wash all clothing, towels and bedding used in the last three days before beginning treatment.
Your doctor will probably instruct you to apply the medication at night when the mites are most active. You may need to treat all of your skin from the neck down. Your doctor will likely be able to diagnose scabies simply by performing a physical exam and inspecting your affected area of skin. In some cases, your doctor may want to confirm the diagnosis by removing a mite from your skin with a needle. It’s important to treat a pet with mange since you and your pet will continue to come into contact with these mites until they’re treated. Scabies is the result of an infestation of tiny, eight-legged mites.
Symptoms of crusted scabies include thick crusts of skin that contain large numbers of scabies mites and eggs. There have been some studies that suggest that neem is effective in treating scabies because it kills the mites. However, transmission can occur even after brief skin-to-skin contact, such as a handshake, with a person who has crusted scabies. In general, a person who has skin-to-skin contact with a person who has crusted scabies would be considered a good candidate for treatment.
The usual severe itch and rash may be absent in people with crusted scabies. Crusted scabies infestations are particularly problematic for older people, people who are immunosuppressed, and people who are frail or weak. There are a variety of different skin conditions that can appear similar to a scabies rash. People should reconsider the use of medical interventions if their condition does not get any better with at-home treatments. Anyone in direct contact with someone who has scabies is at risk of developing an infestation. Sexual partners, friends, and family members are at high risk of developing the condition.

Archeological evidence from Egypt and the Middle East suggests scabies was present as early as 494 BC. In the fourth century BC, Aristotle reported on "lice" that "escape from little pimples if they are pricked" – a description consistent with scabies. Arab physician Ibn Zuhr is believed to have been the first to provide a clinical description of the scabies mites. The symptoms are caused by an allergic reaction of the host's body to mite proteins, though exactly which proteins remains a topic of study. The mite proteins are also present from the gut, in mite feces, which are deposited under the skin.

No comments:
Post a Comment